The Gladys Valley Marine Studies Building is engineered to survive a magnitude 9.0+ earthquake and resulting tsunami. Its rooftop is designed to be an emergency assembly site for more than 900 people after an earthquake.
An Engineering Model for Coastal Communities

The Gladys Valley Marine Studies Building (GVMSB) is designed to provide a safe place for people to gather after an earthquake, out of the path — and above the water — of a possible tsunami.
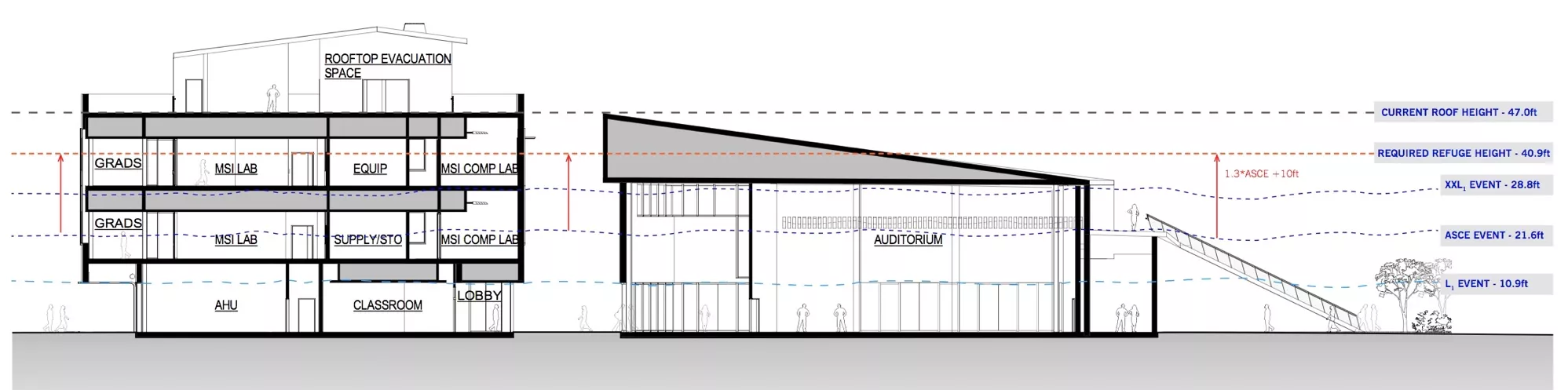
This heavily engineered building offers a vertical evaluation structure with supplies on the rooftop to support over 920 people for up to two days following a Cascadia-level event. This building is designed to withstand a 9+ earthquake and to survive an XXL tsunami event. The building is also designed to be repairable after a large (L) tsunami event. The addition of the GVMSB improves the safety of the people who work and play at Hatfield and in the surrounding South Beach community.
The Hatfield campus also offers two ground-level evacuation routes people can walk to avoid a tsunami inundation event. These routes go to Safe Haven Hill west of Highway 101 and the Oregon Coast Community College to the south. Learn about these evacuation options by participating in the HMSC Tsunami Options Quest (pdf), a free-choice learning activity that uses clues to teach people about a place or event.
Building Access and Features
This building is specially designed to resist earthquake and tsunami forces. There are three roof access points: a ramp, stairs, and an emergency elevator with backup power to help people get to the rooftop assembly area above the height of tsunami waves.
Accessing the roof
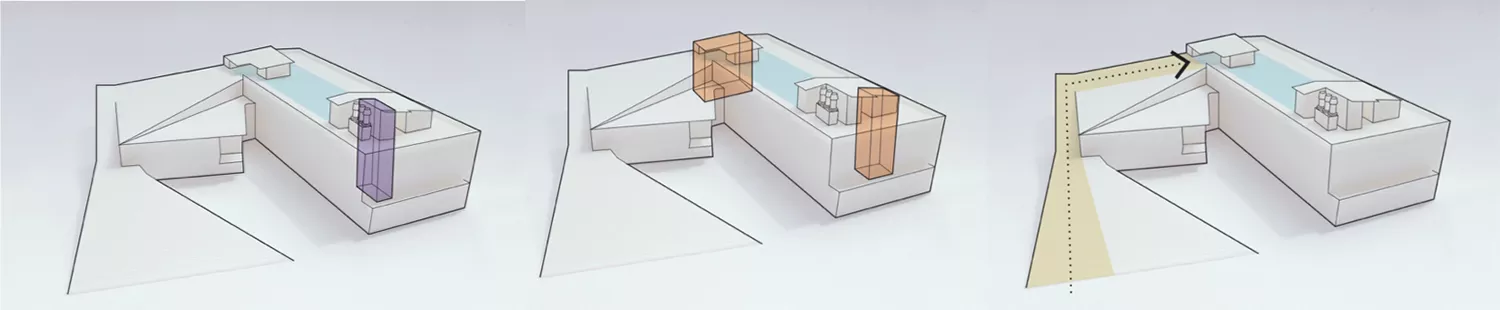
- Ramp: A ramp on the outside of the GVMSB leads from the ground level to the roof (47 feet high). The sloped walkway outside is the most obvious of three rooftop access points. It is designed to be seen, and its purpose is clear. The public can access it 24/7.
- Stairs: There are two sets of stairwells within the GVMSB that lead to the roof.
- Emergency Elevator: This elevator enables people with limited mobility to evacuate the area. An elevator is available 24/7 to take people to the top of the building. It is designed to operate on emergency power and will accommodate as many as 200 people in the 20-minute window between an earthquake and a tsunami. The emergency elevator is equipped with backup power. This elevator makes the GVMSB an ADA-approved accessible vertical evacuation structure.
Community Disaster Cache
On the roof is a cache filled with survival supplies to support 920 people for two days. It includes water, food, sanitation, shelters, communication, personal warmth, lighting, and trauma first aid supplies.
Designed for Safety
Two Buildings in one
The Gladys Valley Marine Studies Building is actually two buildings built with a small V-shaped gap between them. This gap allows each wing to move independently during an earthquake.
Progressive Collapse
The structural steel columns are designed to be compromised and not impact the life-saving function of the roof.
Crumple Zone
The building's design includes a "bumper" around the building to maintain structural integrity when tsunami-carried debris strikes the building. The guardrail on the roof marks the location of offset structural I-beams.
Wall Construction
The nonstructural walls are designed to wash out when struck by the force of the tsunami waves. However, this will not alter the integrity of the rooftop assembly area.
Deep Soil Mixing
There are 250 vertical panels under the building in a grid pattern. These panels were made by mixing cement grout into the soil. The panels create a friction foundation nearly 100 feet deep, roughly twice as deep as the height of the building. This design will stabilize the soft soils under the building created from liquefaction during the earthquake. It will also help avoid washing out under the building during the tsunami.
Anchors
There are six 50-foot hold-down rods along the center of the building and 44 30-foot hold-down rods around the lab wing. These anchor the building to the foundation panels so it can resist a tsunami's impact and the buoyancy uplift of water forces.
Shear Walls and Cores
The walls around the elevator, stairs and under the ramp are hardened with rebar and concrete. They are also tied to the foundation panels. These walls are designed to allow movement during the earthquake and handle the lateral force of the tsunami waves while maintaining structural integrity.
Three ways to Access
Schematics of the three options for accessing the rooftop evacuation area are pictured below.
Building Facts
Located at the Gladys Valley Marine Studies Building on the Hatfield Marine Science Center campus in Newport, Oregon, adjacent to Yaquina Bay.
$61.7 million building costs
The 72,000 square-foot building includes a three-story academic and research center connected to a two-story wing with community space, an auditorium and other facilities.
Construction began in March 2018 and the building was completed in 2020.
Yost Grube Hall, architects; Andersen Construction, general contractor.
Unique Foundations
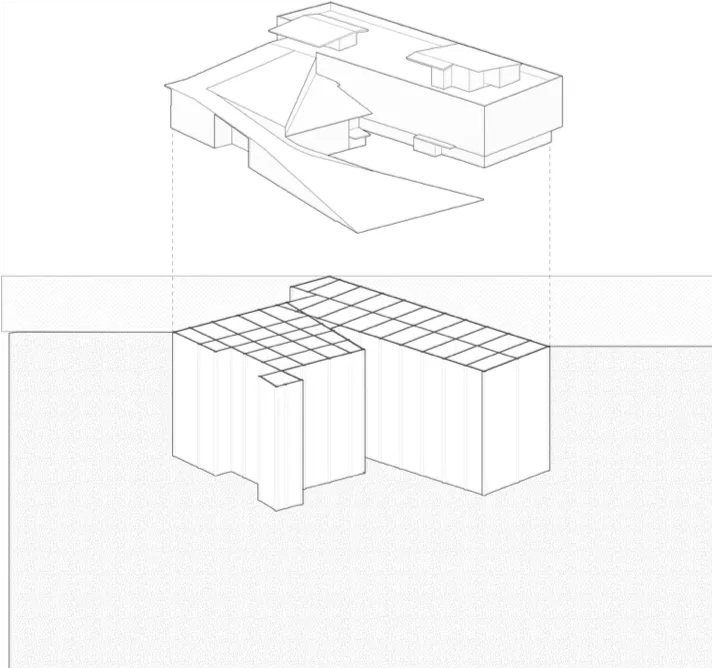
Deep-soil mixing is a technique used to stabilize the ground under a building. Augers are used to pull out existing soil and replace it with cement grout. In the case of the GVMSB, the augers went nearly 100 feet below ground and used approximately 27,380 cubic yards of grout. The video clip below captures this process.